The Unit Cell
This section deals with the geometry of crystaline systems. These could describe how metal atoms pack when they form metallic solids, or how ions pack when they form ionic crystals. We will look at the ionic structures in the next section, and here focus on the generic unit cell and it's application to metallic structures.
There are 7 types of unit cells, defined by edge lengths (a,b,c) respectively along the x,y,z axis and angles α, β, and γ. In this class we will only focus on the cubic unit cell, and there are three types of cubic cells that you need to be familiar with, and these are represented in figure 12.1.b.
- α = angle in the yz plane
- β = angle in the xz plane
- γ = angle in the xy plane
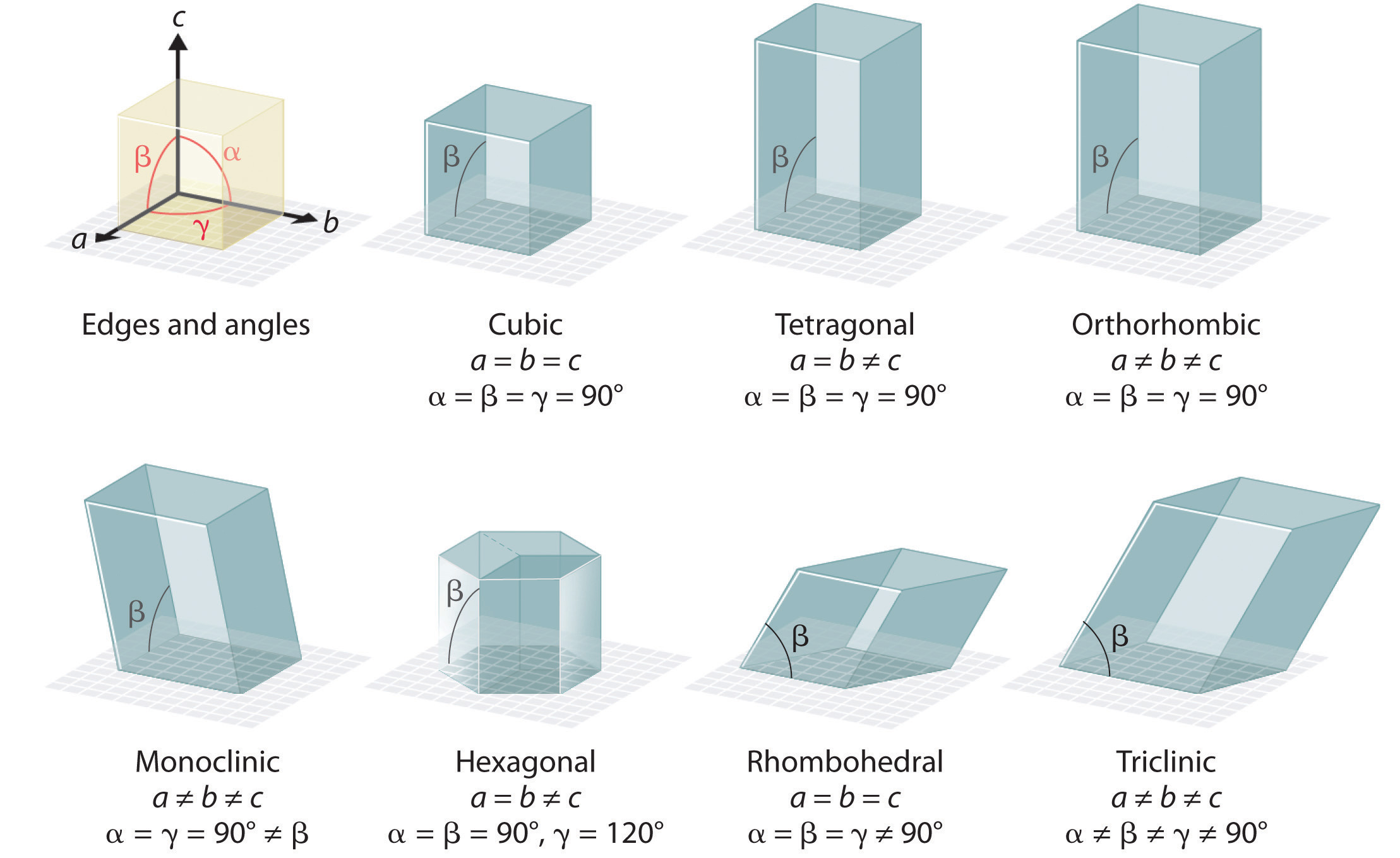
The 7 types of unit cells. In this class we will only look at cubic systems, and will identify 3 types of cubic unit cells
